Toyota is planning to build a new EV battery plant on Japan’s “Silicon Island” to keep pace with BYD and other incoming Chinese electric car makers. The factory will strengthen Toyota’s EV supply chain while supplying batteries for its luxury Lexus brand.
Although Toyota has been one of (if not the) biggest laggards in the global shift to electric cars, the Japanese automaker realizes it needs to compete with Chinese EV makers like BYD.
After launching its first EV, the Atto 3, in Japan, BYD now has three EVs rolling out on Toyota’s home turf. BYD launched its Tesla Model 3 rival Seal EV last month, starting at ¥5.28 million, or around $33,100.
According to the Japan Automobile Importers Association (JAIA), Chinese EV imports accounted for nearly 10% of all cars shipped into Japan in the first half of 2024.
And Japan is not an easy market to break into. Toyota and other domestic automakers dominate Japan’s auto sales, while most imports are European luxury like BMW, Mercedes, and Porsche.
BYD was the prime reason behind the growth, with passenger car imports surging 184% compared to last year.
Toyota looks to counter BYD’s surge with a new EV battery plant in Kyushu, the southernmost island of Japan’s main four.

Toyota to build a new EV battery plant in Japan
According to Nikkei, Toyota’s battery manufacturing business, Primeearth EV Energy, will operate the new plant.
The island is home to several auto and semiconductor plants, earning it the nickname “Silicon Island.” Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. (TSMC), the largest global contract chipmaker, just opened its second plant on the island.

Toyota’s new plant will help boost exports to Asia, building out its EV supply chain. The site is 25 miles (40 km) from Toyota’s Miyata plant, which builds Lexus vehicles, mainly for export.
According to the report, the facility will be the main supplier for its Miyata plant. The plant has up to 430,000 annual capacity, 90% of which are exported.

With most going to Asia, Toyota aims to secure its position in the shifting market. BYD and other Chinese EV makers are expanding their presence in Asia with advanced, low-cost EVs.
By building the batteries near its Miyata plant, Toyota can avoid unnecessary shipping expenses and critical time.
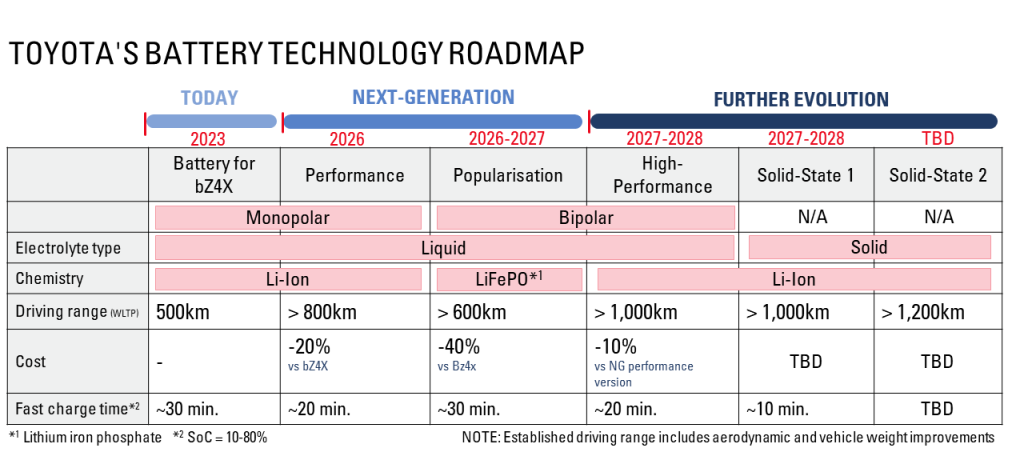
The company plans to invest $32 billion (5 trillion yen) in EVs by 2030, much of it going toward batteries. By then, Toyota aims to sell 3.5 million EVs annually. Last year, it sold 104,000.
Toyota has yet to reveal how much it will spend on the new EV battery plant or when construction will kick off, but more details are expected soon. Check back soon for the full scoop.


